How to Preserve Muscle When Intermittent Fasting

Hey Angels and Alphas,
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity as an effective approach for weight management, improved metabolic health, and increased energy levels.
While it has numerous benefits, one concern that arises with intermittent fasting is the potential loss of muscle mass. Many people worry that fasting for extended periods might lead to muscle breakdown and hinder their fitness goals.
However, with the right strategies, it’s possible to preserve muscle while reaping the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Because yes, we all want the benefits of fasting, but we don’t want to lose the muscle we work so hard for.
In this article, we’ll explore how to maintain lean muscle mass while practicing intermittent fasting.
Let’s get right into it!
Understanding Intermittent Fasting
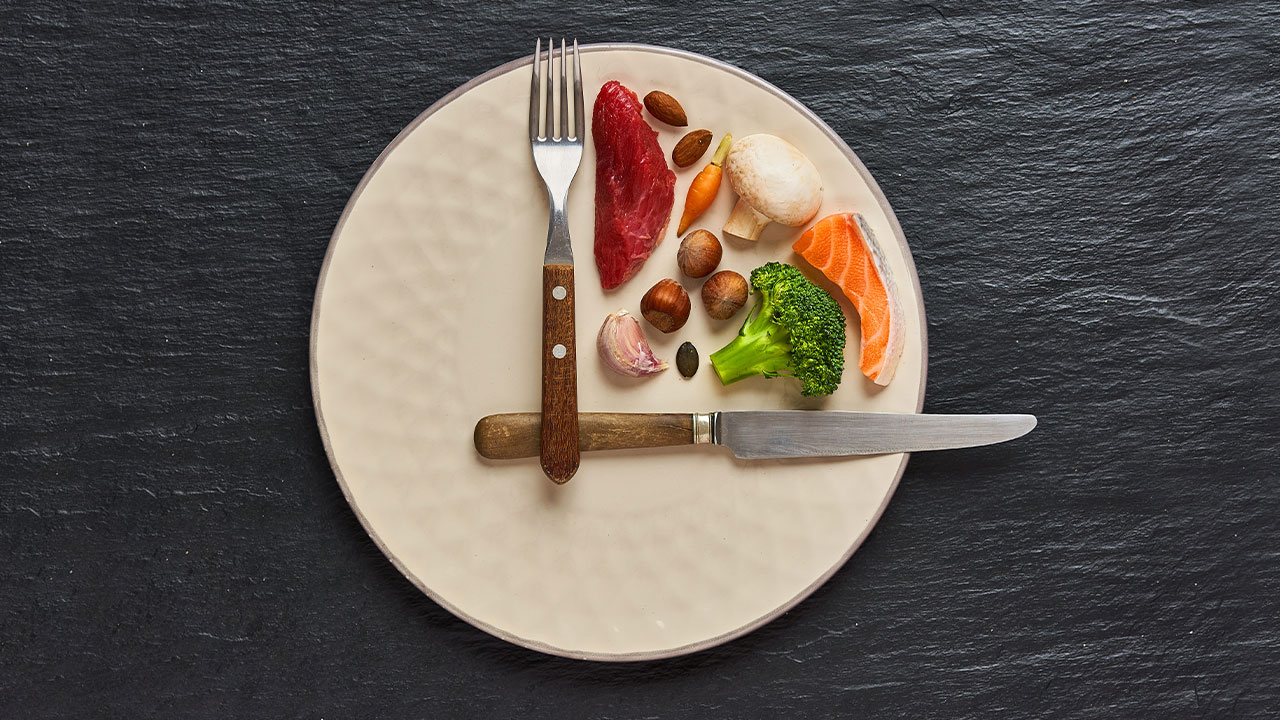
Intermittent fasting is not a diet per se; it is an eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. The most common methods include the 16/8 method (16 hours of fasting and an 8-hour eating window) and the 5:2 method (five days of regular eating and two non-consecutive days of restricted calorie intake). During the fasting phase, the body relies on stored energy, including glycogen and fat, for fuel.
The Muscle Preservation Challenge
When the body is in a fasting state, there is a concern that it may break down muscle tissue to supply amino acids for energy. Muscle protein breakdown occurs when there is an imbalance between protein synthesis (building of muscle) and protein degradation (breaking down of muscle). To prevent muscle loss during intermittent fasting, it is crucial to address this imbalance.
1. Sufficient Protein Intake
Protein is the building block of muscle, and consuming an adequate amount is essential for muscle preservation during intermittent fasting. Aim to include high-quality protein sources in your meals. Foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, tofu, and tempeh are excellent sources of protein. Consider dividing your protein intake evenly across your eating window to optimize muscle protein synthesis.
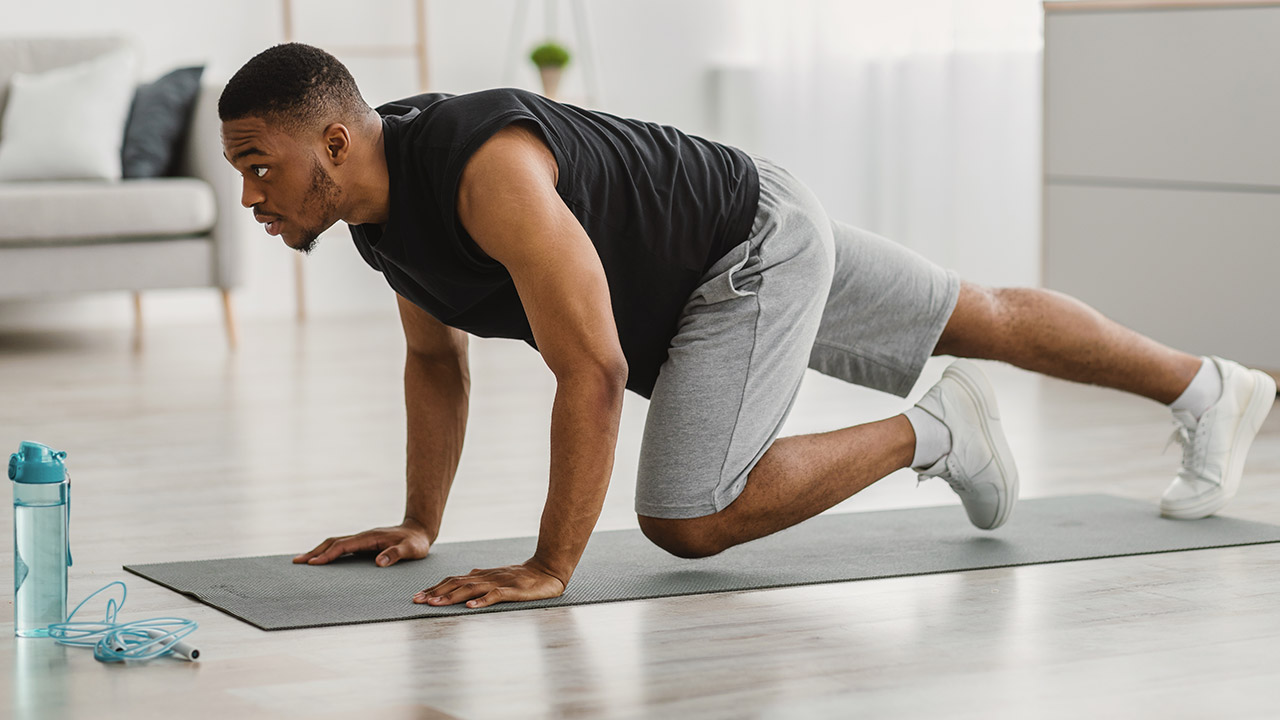
2. Resistance Training
Engaging in regular resistance training is one of the most effective ways to preserve muscle mass during intermittent fasting. Resistance exercises like weight lifting, bodyweight exercises, and resistance band workouts stimulate muscle fibers and promote muscle protein synthesis. Prioritize compound movements that engage multiple muscle groups, such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups.
3. Time Your Workouts Wisely
Consider scheduling your workouts towards the end of your fasting period or shortly before breaking your fast. This way, you provide your body with the necessary nutrients and protein immediately after exercise to support muscle recovery and growth.
4. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
BCAAs are essential amino acids that can help preserve muscle during fasting periods. Consuming BCAAs before or during fasting windows can provide the body with a source of readily available amino acids, reducing the risk of muscle breakdown. BCAA supplements are widely available, but whole food sources like whey protein, eggs, and meat also contain BCAAs. Keep in mind, anything with calories will break your fast, so BCAAs will technically break your fast!
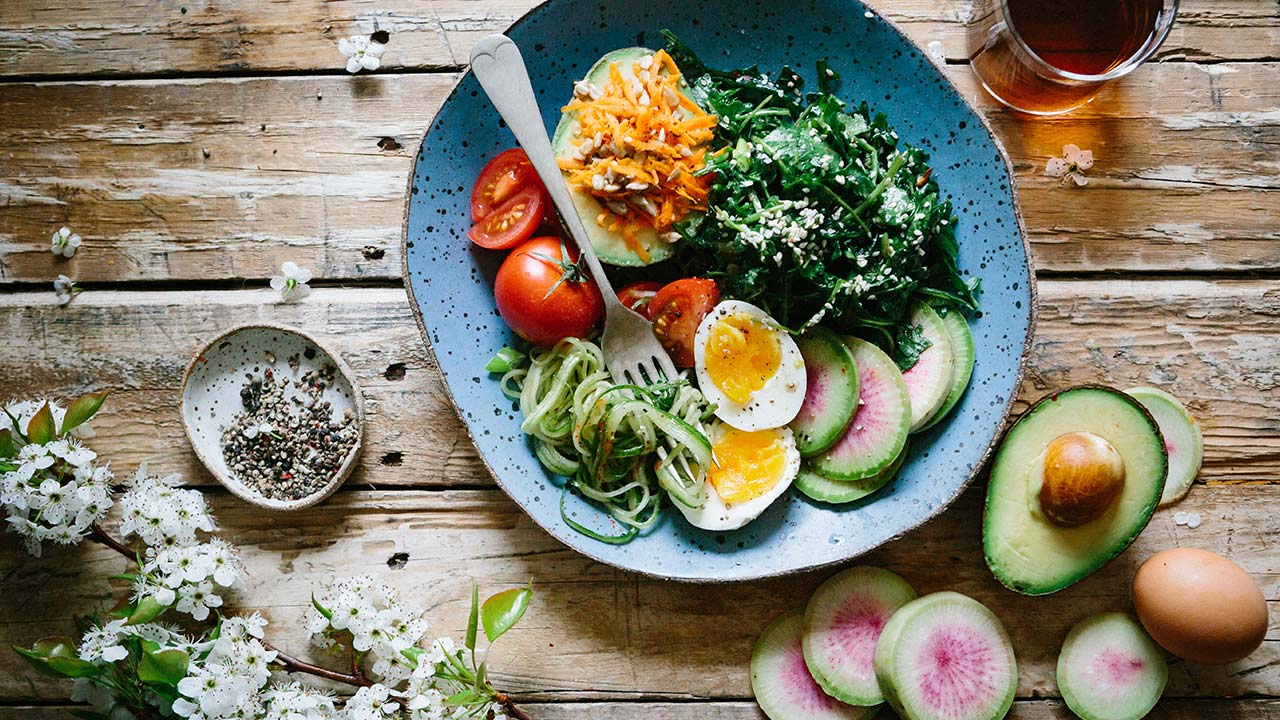
5. Caloric Intake and Nutrient Density
Although intermittent fasting involves periods of calorie restriction, it is vital to ensure that your meals are nutrient-dense when you break your fast. Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats into your eating window to support overall health and muscle preservation.
6. Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is crucial for muscle function and recovery. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, even during fasting periods. Proper hydration can help prevent muscle cramps and improve overall exercise performance.
7. Ultimately, You Might Have to Avoid Prolonged Fasts
To minimize the risk of muscle loss, avoid overly prolonged fasting periods. Extended fasts, especially without adequate protein intake, may lead to muscle breakdown. If you plan to fast for longer durations, consider consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure proper nutrient intake.
Bringing it all together…
Intermittent fasting can be a valuable tool for weight management and overall health.
To preserve muscle while practicing intermittent fasting, prioritize protein intake, engage in resistance training, and time your workouts strategically. Additionally, consider supplementing with BCAAs, stay hydrated, and focus on nutrient-dense meals during your eating window.
With the right approach, intermittent fasting can complement your fitness goals while maintaining lean muscle mass and promoting a healthy lifestyle. As always, individual needs and responses to intermittent fasting may vary, so listen to your body and adjust your approach accordingly.