Why Gaining Weight Doesn’t Mean Gaining Fat

Hey Angels and Alphas,
It’s a common scenario: stepping onto the scale and seeing a five-pound increase can trigger a wave of panic and disappointment.
However, it’s crucial to understand that gaining five pounds does not necessarily mean you’ve gained five pounds of fat. Weight fluctuations are normal and can be attributed to various factors that don’t relate directly to body fat.
This article will explore the different reasons behind short-term weight changes and explain why these should not be a cause for immediate concern.
1. It Could be Water Retention!
One of the most common causes of sudden weight gain is water retention. The human body tends to hold onto water for several reasons, such as:
- Salt Intake: Consuming a high-sodium meal can cause the body to retain water.
- Carbohydrate Intake: When you eat carbohydrates, your body stores them as glycogen. Each gram of glycogen comes with about three grams of water.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations associated with the menstrual cycle, menopause, or stress (due to cortisol) can lead to significant water retention.
2. Increased Muscle Mass
If you’ve recently started or intensified your workout regimen, especially with strength training, you might see an uptick on the scale. Muscle is denser than fat, so even if you’re burning fat, increased muscle mass can cause your weight to increase.
3. Food in Your System
The weight of the food and liquid you consume throughout the day contributes to your overall weight at any given moment. For example, a big meal or drinking lots of fluids can add a few pounds until your body has processed and eliminated it.
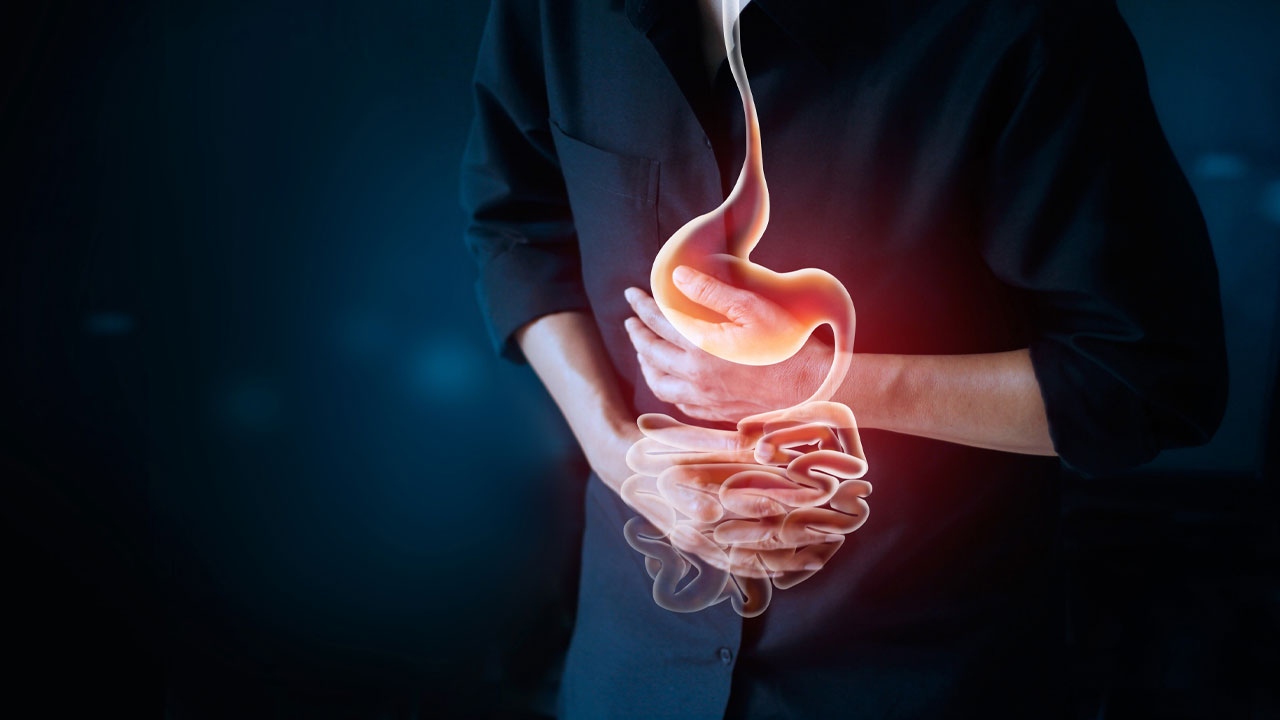
4. Changes in Digestive Contents
Variations in bowel movements can also affect your weight. Constipation can lead to a temporary weight increase, as can variations in fiber intake, which affects how quickly food moves through your digestive system.
5. Medication and Medical Conditions
Certain medications, such as those for blood pressure or psychiatric conditions, can lead to weight gain as a side effect. Additionally, medical conditions like hypothyroidism or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also cause sudden weight gain due to hormonal imbalances affecting metabolism.
Conclusion
Seeing an increase on the scale is not necessarily a sign of fat gain. Weight fluctuates daily and can be influenced by a range of factors including water retention, muscle mass, the physical weight of your meals, digestive changes, and more.
Understanding these factors can help you maintain a more balanced and less stressful relationship with your scale.
For those who track their weight as part of managing health or fitness, consider looking at longer-term trends rather than day-to-day changes. Consistent monitoring over weeks or months can provide a more accurate picture of your true weight status.
Remember, weight is just one metric of health and not a definitive measure of body composition, fitness, or overall well-being.
Always consider holistic aspects of health and consult with healthcare professionals when concerned about sudden weight changes.